Tel : 94870 36000, 94860 36000, 94890 36000
What is Tibial Interlocking Nail and How Does It Work?
The Tibial Interlocking Nail is a pivotal innovation in orthopedic surgery. This device aids in the stabilization of tibial fractures. Understanding its function is crucial for both surgeons and patients.
When a patient suffers a tibial fracture, treatment options vary. The Tibial Interlocking Nail offers a minimally invasive solution. Surgeons insert the nail into the tibia, providing internal support. This method reduces recovery time and improves outcomes.
However, not every case is ideal for this technique. Some fractures may require alternative methods. Patients should be aware of potential complications, such as infection or improper alignment. Overall, the Tibial Interlocking Nail represents a significant advancement, yet reflection on its limitations is essential. Effective communication between patients and providers is necessary for successful treatment.
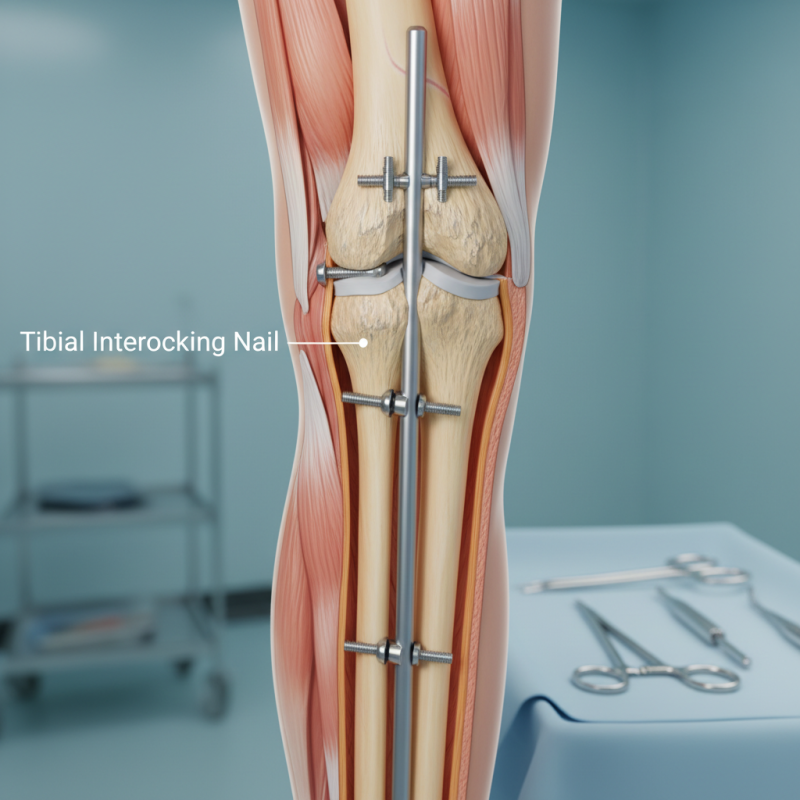
Table of Contents [Hide]
What is Tibial Interlocking Nail?
The Tibial Interlocking Nail is a specialized medical device used in orthopedic surgery. It provides internal fixation for fractures in the tibia, the larger bone in the lower leg. The design features interlocking screws that stabilize the bone and promote healing. According to recent studies, this method reduces the risk of nonunion and complications compared to traditional external fixation.
When applied, this nail is inserted through the medullary canal of the tibia. Surgeons use fluoroscopy to guide its placement accurately. Research shows that this technique can lead to faster recovery times. Patients with tibial fractures often resume normal activities within months. However, achieving precise alignment during insertion can be challenging. Some surgeons report a learning curve with the procedure.
Despite the advantages, there are concerns. Complications such as infection or improper alignment can arise. Data suggests that approximately 10-15% of patients may experience adverse outcomes. Continuous improvement in surgical techniques and training is essential. More research is needed to minimize risks and enhance effectiveness. Overall, the Tibial Interlocking Nail represents a significant advancement in fracture management. It's a method that blends technological innovation with surgical art, but it still requires careful application.
The Structure and Design of Tibial Interlocking Nails
Tibial interlocking nails are fascinating orthopedic devices. They are designed to stabilize broken tibias. The structure consists of a long metal rod, which is inserted into the medullary canal of the bone. This rod has holes for screws, allowing secure fixation. Each nail is made of durable materials, often titanium or stainless steel.
The design enhances healing by minimizing movement at the fracture site. When inserted correctly, these nails distribute weight evenly. This helps patients return to normal activities sooner. They are also adjustable, accommodating various fracture types. However, improper sizing can lead to complications. It’s essential to choose the right length and diameter.
Some patients experience discomfort after installation. This may require adjustments or even removal. Reflection on these experiences can improve future applications. While the tibial interlocking nail is an effective solution, challenges still exist. Addressing these issues is crucial for better patient outcomes.
Tibial Interlocking Nail - Usage and Success Rate
Indications for Using Tibial Interlocking Nails in Surgery
Tibial interlocking nails are a crucial tool in orthopedic surgery. They are primarily used for stabilizing fractures in the tibia, especially in cases where the bone is unstable. Indications for using these nails include long bone fractures, particularly in cases of open fractures where stabilization is needed urgently. According to a report by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, these nails improve healing time by providing strong internal fixation.
Understanding the specific cases where tibial interlocking nails are beneficial can enhance surgical outcomes. Surgeons often recommend their use in proximal, mid-shaft, and distal tibial fractures. The interlocking feature prevents rotational and axial instability. This is vital in cases involving high-energy trauma or when the fracture type is complex. A study showed that patients treated with interlocking nails had a 90% success rate in achieving bony union within six months.
Tips: Always assess the patient's overall health before surgery. Comorbid conditions can affect healing rates. Additionally, thorough imaging is essential. It ensures correct nail positioning. Proper nail length and diameter selection is crucial. Incorrect sizing can lead to complications. Remember, the key lies in precise surgical technique and careful patient management.
What is Tibial Interlocking Nail and How Does It Work? - Indications for Using Tibial Interlocking Nails in Surgery
| Indication | Description | Patient Profile | Surgical Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fracture of the Tibia | Used for stabilization of complex tibial fractures. | Adults with mid-shaft tibial fractures. | Provides strength and allows early mobilization. |
| Non-Union of Tibial Fractures | Corrects and stabilizes fractures that fail to heal on their own. | Patients with history of delayed healing. | Enhances union rates and functional outcomes. |
| Open Fractures | Provides stabilization while allowing for surgical irrigation and debridement. | Patients with open tibial fractures due to trauma. | Promotes healing while managing soft tissue injuries. |
| Revision Surgery | For patients needing complex revision due to prior failed surgery. | Patients with previous hardware issues or persistent pain. | Reduces pain and improves function through stable fixation. |
How Tibial Interlocking Nails Are Inserted and Secured
Tibial interlocking nails are crucial for stabilizing tibial fractures. The insertion process begins with a precise alignment of the nail within the medullary canal. A drill is used to create an entry point, often around the knee region. This access allows the nail to be inserted and carefully guided down the shaft of the tibia.
Once in place, locking screws are added through pre-drilled holes in the nail. These screws secure the nail to the bone, preventing movement at the fracture site. Studies indicate that this technique significantly reduces non-union rates. According to research, the incidence of complications is about 5% to 10%, highlighting the importance of expertise in the procedure.
While tibial interlocking nails improve outcomes for many patients, challenges remain. In some cases, the alignment may not be perfect, leading to malunion. Surgeons must be vigilant during the entire process. Techniques continue to evolve, as advancements in materials and methods are ongoing. The importance of post-operative monitoring cannot be overstated. Each case of tibial fracture presents unique considerations that surgeons must evaluate carefully.
Benefits and Risks Associated with Tibial Interlocking Nail Procedures
Tibial interlocking nails are used to treat fractures in the tibia. This procedure involves inserting a metal rod into the bone. It stabilizes the fracture and aids in healing. While effective, there are benefits and risks to consider.
One major benefit is improved stability. The intramedullary nail provides strong support to the bone. It allows for early weight-bearing, which can speed up recovery. However, complications can arise. Infection at the surgical site is one risk. There might also be issues like delayed healing or non-union of the fracture. Patients must weigh these risks against the benefits.
Tips: Always discuss your options with your healthcare provider. Ask about the likelihood of complications. Make sure to follow post-operative care instructions closely. It’s crucial to monitor for signs of infection or abnormal pain levels. Recovery can be frustrating, and it's important to maintain realistic expectations. Holistic healing involves both physical and emotional aspects. A support system can significantly aid in recovery.